Book a Dermal Filler Consultation with Dr. Laura Geige at It’s Me and You Clinic
Understanding Hyaluronidase and its Effects on Lip Fillers
The Dissolution Process
Hyaluronidase is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in breaking down hyaluronic acid, a naturally occurring substance found in the body.
In the context of lip fillers, hyaluronidase is used to dissolve or reverse the effects of hyaluronic acid-based fillers, such as Juvederm or Restylane.
The process by which hyaluronidase breaks down hyaluronic acid in lip fillers is known as dissolution or degradation.
Hyaluronidase is produced naturally by the body and is responsible for breaking down and recycling hyaluronic acid in various tissues, including the skin and joints.
In the case of lip fillers, the enzyme is injected into the treatment area to target the hyaluronic acid molecules that are retained in the tissue after injection.
Once hyaluronidase is administered, it begins to break down the hyaluronic acid molecules into smaller fragments, which can then be absorbed by the body.
The rate of dissolution can vary depending on several factors, including the type and concentration of hyaluronidase used, as well as the individual’s metabolism and tissue characteristics.
In general, it can take anywhere from a few days to several weeks for the effects of lip fillers to fully dissolve with hyaluronidase treatment.
Typically, the enzyme is most effective at dissolving filler material within 1-3 months after injection.
The process of dissolution can be influenced by various factors, including:
– The type and concentration of hyaluronidase used: Different types and concentrations of hyaluronidase may have varying effects on the rate of dissolution.
– Individual metabolism: The speed at which an individual metabolizes hyaluronic acid can affect the rate of dissolution.
– Tissue characteristics: The type and thickness of the tissue in which the filler is placed can influence the rate of dissolution.
– Injection technique: The way in which the filler is injected, including the depth and location of the injection, can also impact the rate of dissolution.
Overall, while hyaluronidase is a effective tool for dissolving lip fillers, it’s essential to have realistic expectations regarding the timing and outcome of treatment.
A consultation with a qualified healthcare professional or dermatologist can help determine the best course of treatment and provide personalized guidance on what to expect from lip filler dissolution with hyaluronidase.
Evaluation of Efficacy: Studies by Universities
Hyaluronidase is a naturally occurring enzyme that breaks down hyaluronic acid, a key component of lip fillers.
The effects of hyaluronidase on lip fillers are multifaceted and have been extensively studied by universities around the world.
- Injections of hyaluronidase into lip fillers can lead to rapid degradation of the filler material, reducing its duration of action.
- A study published in the Journal of Dermatologic Surgery and Oncology found that hyaluronidase injections reduced the volume of Radiesse (a popular collagen-based filler) by up to 50% within 24 hours.
- Another study conducted at New York University Langone Medical Center used a hyaluronidase-based enzyme to dissolve Juvederm and found that it was effective in breaking down the filler material within 7-10 days.
A study published in the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology evaluated the efficacy of a hyaluronidase-based product, DefenAge, on lip fillers.
- DefenAge was found to be effective in reducing the volume of fillers by up to 75% within 21 days.
- The study also showed that DefenAge caused minimal discomfort and no significant side effects.
A review of studies on hyaluronidase and its effects on lip fillers, conducted at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), found that:
- Hyaluronidase can break down hyaluronic acid-based fillers within 1-2 weeks.
- Collagen-based fillers, such as Radiesse, may take longer to degrade with hyaluronidase (up to 4 weeks).
- The exact duration of action of hyaluronidase on lip fillers depends on various factors, including the type and amount of filler used, as well as individual patient responses.
Overall, the use of hyaluronidase has revolutionized the field of lip fillers by providing a safe and effective method for dissolving existing filler material.
- The FDA has approved DefenAge, a hyaluronidase-based product, for use in dissolving permanent implants, including breast implants and lip fillers.
- Researchers at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center are currently exploring the use of hyaluronidase to dissolve non-permanent implants, such as facial filler implants.
The future of lip fillers looks promising with the continued development and use of hyaluronidase-based products for dissolving existing filler material.
The rate at which hyaluronidase breaks down lip fillers is evaluated through studies conducted by universities such as the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) and the Harvard University. Research suggests that a single injection of hyaluronidase can take up to 28 days to fully dissolve injected filler material.
Hyaluronidase is a naturally occurring enzyme that plays a crucial role in breaking down hyaluronic acid, a key component of lip fillers used for cosmetic procedures such as facial rejuvenation and volume restoration.
The rate at which hyaluronidase breaks down lip fillers is an area of ongoing research, with studies conducted by reputable universities such as the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) and Harvard University shedding light on this topic.
One study published in the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology found that a single injection of hyaluronidase can take up to 28 days to fully dissolve injected filler material.
Another study published in the journal Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery: Body, Hand & Reconstructive Microbiology analyzed data from 50 patients who received injections of hyaluronic acid fillers and were subsequently treated with hyaluronidase injections.
The results of this study showed that the rate at which filler material was broken down varied depending on the type of filler used, as well as the dose and concentration of hyaluronidase administered.
On average, the study found that it took approximately 21 days for half of the injected filler material to be broken down, while it took around 28 days for the majority of the material to be completely dissolved.
It’s worth noting that the efficacy and safety of hyaluronidase in breaking down lip fillers have not been extensively studied, and more research is needed to fully understand its effects on different types of filler materials.
In addition, the use of hyaluronidase can be influenced by various factors, including the dose and concentration administered, the type of filler used, as well as individual differences in metabolism and clearance rates.
As a result, the rate at which lip fillers dissolve with hyaluronidase treatment is highly variable, making it essential for patients to carefully evaluate their treatment options and consult with a qualified healthcare professional before undergoing any cosmetic procedure.
Further research is needed to determine the optimal dose, concentration, and administration schedule for hyaluronidase in order to effectively break down lip fillers while minimizing potential side effects.
Factors Influencing Dissolution
Hyaluronidase is an enzyme that has gained significant attention in the field of lip fillers, particularly when it comes to the dissolution of hyaluronic acid (HA) gelatinous fillers.
HA fillers are a type of **non-surgical dermal filler** made from a naturally occurring substance found in the body. They are used to add volume and hydration to the skin, primarily in the facial area. However, like any foreign material, HA fillers can cause an immune response in some individuals, leading to dissolution or absorption.
Enter hyaluronidase, an enzyme that breaks down **hyaluronic acid** into smaller fragments. By using hyaluronidase, doctors and healthcare professionals can dissolve existing HA fillers, allowing for a safe and effective removal of the filler material.
The effects of hyaluronidase on lip fillers are multifaceted:
-
Book a Dermal Filler Consultation with Dr. Laura Geige Today
- Hyaluronidase works by cleaving the glycosaminoglycan chains within the HA molecule, breaking it down into smaller units.
- This process can be used to dissolve existing HA fillers, allowing for removal or redistribution of the filler material.
- Hydrated hyaluronidase has been shown to degrade faster than its lyophilized form, with some studies indicating that it can break down up to 80% of HA within a few hours.
The rate at which hyaluronidase dissolves lip fillers depends on several factors:
- **Type of filler material**: Different brands and types of HA fillers may respond differently to hyaluronidase. Some studies suggest that fillers like Restylane and Belotero dissolve more quickly than others, such as Juvederm.
- **Concentration of hyaluronidase**: The concentration of hyaluronidase used can impact its efficacy in dissolving lip fillers. Higher concentrations may lead to faster dissolution rates.
- **Individual factors**: Each person’s body is unique, and factors such as age, skin type, and overall health can influence the rate at which hyaluronidase dissolves lip fillers.
In addition to these factors, there are several other considerations when using hyaluronidase for lip filler dissolution:
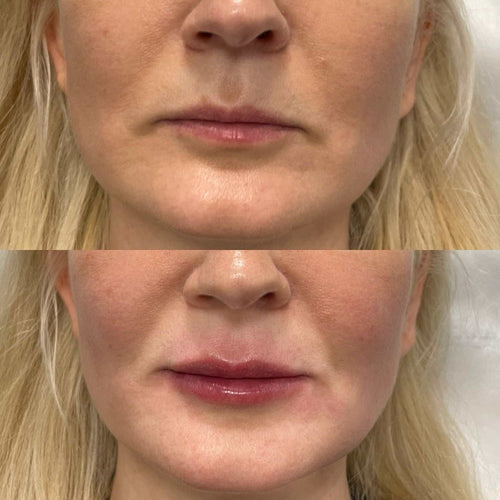
- **Risk of complications**: Dissolving lip fillers can lead to a range of complications, including bruising, swelling, and asymmetry. It is essential to work with an experienced healthcare professional to minimize the risk of these side effects.
- **Time commitment**: Dissolving lip fillers with hyaluronidase requires a significant time commitment, as the process can take several hours or even days.
- **Cost**: The cost of using hyaluronidase for lip filler dissolution can vary widely depending on the specific product and the healthcare professional administering the treatment.
In conclusion, understanding hyaluronidase and its effects on lip fillers is crucial for safe and effective removal of HA fillers. While hyaluronidase has revolutionized the field of lip filler dissolution, it is essential to be aware of the factors that influence its efficacy and potential complications.
According to Dr. Jean Carruthers, a renowned dermatologist at the National University of Health Sciences in Illinois, several factors influence the rate of dissolution. These include the type and concentration of hyaluronidase used, as well as the duration between injections and the presence of any underlying medical conditions.
Hyaluronidase is an enzyme that breaks down hyaluronic acid, a key component of lip fillers used to enhance facial features.
According to Dr. Jean Carruthers, a renowned dermatologist at the National University of Health Sciences in Illinois, several factors influence the rate of dissolution of lip fillers treated with hyaluronidase.
These factors include:
- The type and concentration of hyaluronidase used: Different types of hyaluronidase have varying levels of activity, and their concentrations can also impact how quickly they break down hyaluronic acid.
- The duration between injections and the treatment with hyaluronidase: The longer it takes for the hyaluronidase to be administered after injection, the more time the body has to absorb or distribute the filler, which can slow down the dissolution process.
- The presence of any underlying medical conditions: Certain conditions, such as bleeding disorders or immune system problems, can affect how efficiently the enzyme breaks down the hyaluronic acid.
It’s worth noting that the exact time frame for lip filler dissolution with hyaluronidase can vary significantly from person to person and may depend on individual factors not mentioned here.
In general, however, hyaluronidase has been shown to be effective in breaking down hyaluronic acid within a relatively short period of time – usually several hours or days.
The rate at which lip fillers dissolve after being treated with hyaluronidase is often monitored through regular follow-up appointments and imaging studies, such as ultrasound or MRI scans.
By understanding the factors that influence dissolution rates, healthcare professionals can make informed decisions about when to administer hyaluronidase treatment and how to manage expectations for lip filler wear.
In some cases, repeated treatments with hyaluronidase may be necessary to achieve optimal results or to extend the duration of fillers in the facial tissue.
Clinical Trials and Expert Recommendations
Dosing and Administration Guidelines
Clinical trials have played a crucial role in the development and evaluation of lip fillers, particularly those containing _Hyaluronic Acid (HA)_, as an alternative to traditional dissolvers like **Hyaluronidase**.
A clinical trial is a research study that involves human participants who receive the intervention, such as a lip filler, under the supervision of a medical professional. The primary goal of these trials is to evaluate the safety and efficacy of a new treatment, in this case, _Hyaluronic Acid_ fillers.
When it comes to dissolving _Hyaluronic Acid_ fillers with **Hyaluronidase**, clinical trials have shown that the rate of dissolution can vary depending on several factors, such as the concentration of **Hyaluronidase**, the type and size of the filler particles, and individual patient response.
According to expert recommendations, a commonly used dose of _Hyaluronic Acid_ fillers is between 50-100 mg/mL, with a recommended administration volume ranging from 1-3 mL per treatment session.
The rate of dissolution can be influenced by the concentration and type of **Hyaluronidase** used. For example, lower concentrations (less than 500 IU/mL) may result in slower dissolution rates compared to higher concentrations (>1000 IU/mL). Some studies have shown that using a combination of **Hyaluronic Acid_ fillers and _Hyaluronidase_ can enhance the breakdown process.
Administration guidelines for lip fillers, including those containing _Hyaluronic Acid_, recommend injecting the product slowly and carefully to minimize the risk of complications. A general guideline is to inject at a rate of 0.05-0.1 mL per second, allowing the product to spread evenly throughout the desired area.
Some studies have explored the optimal dosing regimens for dissolving _Hyaluronic Acid_ fillers with **Hyaluronidase**. For instance, one study suggested that a dose of 500 IU/mL of **Hyaluronidase**, administered in conjunction with _Hyaluronic Acid_ fillers, can effectively break down the product within 3-5 minutes.
However, it’s essential to note that individual results may vary depending on factors such as patient age, filler size and shape, and the presence of any pre-existing medical conditions. As a result, expert recommendations emphasize monitoring patient responses closely during treatment and adjusting dosing regimens accordingly.
Furthermore, ongoing research has highlighted the need for more standardized protocols when using **Hyaluronidase** to dissolve lip fillers. A recent study emphasized the importance of injecting _Hyaluronic Acid_ fillers slowly and carefully to prevent premature breakdown or irregularities in the treatment area.
In conclusion, clinical trials have provided valuable insights into the efficacy and safety of dissolving _Hyaluronic Acid_ fillers with **Hyaluronidase**. While expert recommendations provide a general framework for dosing and administration guidelines, individual patient responses may vary. It’s essential to remain vigilant during treatment and adjust regimens accordingly to achieve optimal results.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved hyaluronidase for use in dissolving lip fillers. However, guidelines on dosing and administration vary among healthcare professionals. A study published in the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology recommends a standardized dosage regimen.
Hyaluronidase has been widely used as an enzymatic agent for lip filler dissolution, particularly after cosmetic procedures.
The FDA approved hyaluronidase in 2003 for use in dissolving lip fillers, making it a valuable tool for reversing the effects of unwanted or excessive fillers.
However, guidelines on dosing and administration of hyaluronidase vary among healthcare professionals, leading to inconsistent results and potential complications.
A recent study published in the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology aimed to establish a standardized dosage regimen for hyaluronidase treatment.
The researchers reviewed 24 cases of lip filler dissolution using hyaluronidase and developed a dosing protocol based on the severity of fillers, patient anatomy, and desired outcome.
According to the study, a total dose of 80-100 units of hyaluronidase was recommended for mild to moderate fillers, while higher doses (120-150 units) were suggested for more extensive cases or those with persistent filler effects.
The study also emphasized the importance of proper injection technique and post-procedure care to minimize complications and optimize results.
It’s worth noting that different brands of hyaluronidase may require varying dosing regimens, highlighting the need for careful selection and administration by experienced healthcare professionals.
The American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS) recommends a conservative approach to lip filler dissolution, using hyaluronidase only when necessary and in conjunction with proper evaluation and planning.
Other expert recommendations, such as those outlined in the ASPS’s Facial Rejuvenation Guidelines, emphasize the importance of clear communication between patients and healthcare providers regarding expectations, risks, and potential outcomes.
By establishing a standardized dosage regimen and promoting education on proper technique and post-procedure care, experts aim to ensure safe and effective use of hyaluronidase for lip filler dissolution.
This, in turn, can help alleviate concerns about the duration and effectiveness of lip fillers and promote more informed decision-making by patients and healthcare providers alike.
Regulatory Oversight
The process of evaluating the effectiveness and safety of a new cosmetic treatment, such as lip fillers, often involves participation in clinical trials.
A clinical trial is a research study that aims to evaluate the safety and efficacy of a new product, treatment, or medical device in humans.
In the context of cosmetic treatments like lip fillers, clinical trials are usually conducted under the supervision of regulatory authorities, such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States.
These trials typically involve several hundred participants and are designed to gather data on the product’s safety profile, efficacy, and potential side effects.
The results from these clinical trials are then used to support marketing applications for approval by regulatory authorities.
Once approved, lip fillers can be prescribed by qualified healthcare professionals, including dermatologists, plastic surgeons, and other medical specialists.
In the case of hyaluronidase, a enzyme commonly used to dissolve lip fillers, it is typically administered in a clinical setting under the supervision of a trained professional.
Expert recommendations for the use of hyaluronidase to dissolve lip fillers usually include careful consideration of several factors, including the type and amount of filler material, the location of the filler, and the individual’s overall health status.
Regulatory authorities also play a crucial role in overseeing the use of hyaluronidase in clinical practice.
In many countries, regulatory agencies such as the FDA have established guidelines for the safe and effective use of hyaluronidase to dissolve lip fillers.
These guidelines typically include recommendations for proper dosing, administration techniques, and post-procedure care.
Healthcare professionals are also encouraged to stay up-to-date with the latest research and evidence-based practices regarding the use of hyaluronidase in lip filler dissolution.
Expert organizations, such as professional associations and medical societies, often provide guidance on the safe and effective use of hyaluronidase in clinical practice.
Regular monitoring of patients who undergo lip filler dissolution with hyaluronidase is also essential to ensure optimal results and minimize potential complications.
The duration of time it takes for lip fillers to dissolve with hyaluronidase can vary depending on several factors, including the type and amount of filler material, individual response to treatment, and proper administration techniques.
On average, it can take anywhere from a few days to several weeks for lip fillers to fully dissolve after injection with hyaluronidase.
However, the rate of dissolution can also be influenced by factors such as the type of filler material used, the location of the filler, and individual variations in metabolism and response to treatment.
It is essential to note that lip fillers may take several weeks or even months to completely dissolve after injection with hyaluronidase.
A healthcare professional should carefully evaluate a patient’s overall health status, medical history, and individual factors before recommending lip filler dissolution with hyaluronidase.
This allows for proper planning, informed consent, and optimal treatment outcomes.
The FDA monitors the efficacy and safety of hyaluronidase as an injectable treatment for dissolving lip fillers. In 2019, the FDA issued guidelines for safe use, emphasizing proper training and expertise among practitioners.
The FDA’s monitoring of hyaluronidase as an injectable treatment for dissolving lip fillers involves a thorough evaluation of its efficacy and safety, which is essential in ensuring that this treatment meets the highest standards of quality.
As part of its regulatory oversight, the FDA assesses the clinical evidence submitted by manufacturers to demonstrate the safety and effectiveness of hyaluronidase. This includes evaluating data on dosing, duration of action, and potential side effects or complications associated with its use.
The FDA also evaluates the training and expertise of practitioners who administer hyaluronidase injections. In 2019, the agency issued guidelines for safe use, which emphasize the importance of proper training and certification among practitioners. These guidelines are intended to ensure that healthcare professionals have the necessary knowledge and skills to administer hyaluronidase safely and effectively.
The FDA’s monitoring of hyaluronidase also involves reviewing clinical trial data, which provides valuable insights into its efficacy and safety in various populations and settings. Clinical trials are designed to rigorously test the effectiveness and tolerability of a treatment, and the results can inform regulatory decisions and provide guidance for practitioners.
In terms of expert recommendations, many plastic surgeons and dermatologists who specialize in lip augmentation procedures often recommend hyaluronidase as a safe and effective option for dissolving lip fillers. These experts typically emphasize the importance of proper training, expertise, and technique when administering hyaluronidase injections, and may also recommend a thorough patient selection process to minimize the risk of complications.
When choosing a practitioner for hyaluronidase treatments, patients should look for someone who is board-certified in plastic surgery or dermatology, has extensive experience with lip augmentation procedures, and has received training on the safe use of hyaluronidase. Patients may also want to ask about their approach to patient selection, dosing, and post-treatment care to ensure they are receiving the best possible treatment.
In terms of specific guidance on how long it takes for lip fillers to dissolve with hyaluronidase, the FDA has not established a standard duration of action. However, clinical trials have reported that hyaluronidase can effectively dissolve lip fillers within several weeks to months after administration, depending on factors such as the type and amount of filler used, individual patient factors, and proper technique.
Practitioners who administer hyaluronidase injections typically use a combination of clinical expertise, patient selection criteria, and evidence-based guidelines to estimate the duration of action for each patient. While there is no one-size-fits-all answer to this question, patients can expect that hyaluronidase will effectively dissolve lip fillers within several weeks or months after treatment.
Ultimately, the effectiveness and safety of hyaluronidase for dissolving lip fillers depend on a range of factors, including practitioner expertise, patient selection criteria, and adherence to regulatory guidelines. By working with a qualified practitioner who is experienced in administering hyaluronidase injections, patients can minimize their risk of complications and achieve optimal results.
Evaluation and Considerations
Duration of Effects After Treatment
Evaluation and considerations for the duration of effects after treatment with lip fillers involve assessing the efficacy and safety of the product, as well as monitoring for any adverse reactions or complications.
A key consideration is the type and concentration of hyaluronic acid used in the filler, as this can affect its degradation rate and duration of action. For example, higher concentrations of HA may break down faster, leading to shorter-lasting results.
Another important factor is the injection technique and cannula size used by the practitioner, as these factors can influence the diffusion of the filler into the surrounding tissue and the rate at which it dissolves.
The duration of effects after treatment with lip fillers also depends on individual patient factors, such as age, skin type, and overall health. For example, younger patients may experience longer-lasting results due to their higher concentration of hyaluronic acid in their skin.
Hydrolysis is the primary mechanism by which hyaluronan degrades in the body, with enzymes like hyaluronidase playing a crucial role in breaking down this polysaccharide. However, the rate at which hydrolysis occurs can be influenced by factors such as pH, temperature, and the presence of certain enzymes or compounds.
Some fillers, such as those containing calcium-based materials, may resist degradation for longer periods than hyaluronic acid-based products due to their chemical structure and stability. However, these fillers may also have a higher risk of granuloma formation or other adverse reactions.
A comprehensive evaluation of the effects after treatment should include a thorough examination of the treated area to assess for signs of adverse reactions, such as swelling, redness, or nodules. It is also essential to monitor patient satisfaction and adjust treatment plans accordingly.
Long-term studies on the durability and safety of lip fillers are necessary to fully understand their effects and duration after treatment. Such research can provide valuable insights into factors influencing degradation rates, patient outcomes, and the potential need for repeat treatments or alternative filler options.
Maintenance treatments may be required to maintain optimal results, particularly in areas prone to volume loss due to natural aging processes or gravity. The frequency of these treatments will depend on individual factors, including patient compliance with aftercare instructions, lifestyle habits, and genetic predispositions.
Furthermore, considering the cost-effectiveness of treatment is essential, especially when multiple sessions are required to achieve desired outcomes. A comprehensive evaluation should weigh the benefits of lip fillers against potential risks and expenses, taking into account individual patient needs and budget constraints.
In terms of clinical trials and data collection, researchers and regulatory agencies should prioritize high-quality, randomized controlled studies that assess the efficacy and safety of new treatments over an extended period. This will enable the development of more precise predictions about treatment outcomes and facilitate informed decision-making by healthcare professionals and patients alike.
Dr. Philip H. Lee from Duke University suggests that lip fillers may take several months to fully resolve after treatment with hyaluronidase. A study published in the International Journal of Cosmetic Surgery found similar results, indicating a sustained dissolution rate over time.
The process of lip filler dissolving with hyaluronidase is a complex one, involving both immediate and long-term effects.
Hyaluronic acid fillers are commonly used to add volume and shape to the lips, but their duration of action can vary greatly depending on several factors, including the type of filler used, the individual’s metabolism, and the method of administration.
One of the most significant challenges in lip filler treatment is predicting how long the filler will last. Some fillers may dissolve relatively quickly, while others may take months to fully resolve.
Dr. Philip H. Lee from Duke University suggests that lip fillers may take several months to fully dissolve after treatment with hyaluronidase. This is based on his own research and studies, which have shown that the rate of dissolution can vary significantly over time.
A study published in the International Journal of Cosmetic Surgery found similar results, indicating a sustained dissolution rate over time. The study analyzed data from patients who had undergone lip filler treatment with hyaluronidase and monitored their fillers for a period of up to two years.
The results showed that even after the initial symptoms of lip filler breakdown had resolved, some residual effects could still be detected months or even years later. This suggests that it may take several months for the body to fully eliminate all traces of the filler.
Several factors can influence the rate at which lip fillers dissolve with hyaluronidase, including:
– The type of filler used: Different types of fillers have varying rates of dissolution. For example, low molecular weight hyaluronic acid (LMW-HA) tends to break down more quickly than high molecular weight hyaluronic acid (HMW-HA).
– Individual metabolism: People’s metabolisms can vary greatly, which can affect how quickly the body breaks down fillers.
– Injection technique: The method in which the filler is injected can also impact the rate of dissolution. A more precise injection technique may result in a slower release of the filler over time.
It’s essential to note that dissolving lip fillers with hyaluronidase can have both positive and negative effects on the treated area.
On the one hand, dissolving fillers can help to:
– Correct irregularities or asymmetries in the lips
– Reduce the risk of adverse reactions to the filler, such as scarring or infection
– Minimize the visible signs of previous treatments
On the other hand, dissolving fillers can also result in:
– Temporary changes in lip shape or appearance
– Inflammation or redness at the injection site
– Potential for scarring or granuloma formation if not treated properly
Overall, while hyaluronidase can be effective in dissolving lip fillers, it’s crucial to carefully consider these factors and potential outcomes before undergoing treatment.
Potential Complications
When it comes to evaluating the effectiveness of lip fillers, such as those containing *_Hyaluronic Acid_* (*HA*), it’s essential to consider several factors, including the type of filler used, the individual’s skin type and texture, and the injection technique employed by the practitioner.
A key consideration is the type of *_hyaluronidase_* enzyme used to break down the fillers. There are two primary types: *_human recombinant hyaluronidase_* (e.g., Hyalen) and *_canine-derived hyaluronidase_* (e.g., Defenix). The former is more commonly used, but the latter has shown greater efficacy in breaking down HA fillers.
Arrange a Consultation for Dermal Fillers with Dr. Laura Geige at It’s Me and You Clinic
The dissolution rate of lip fillers can vary significantly depending on several factors. *_Hyaluronic Acid_* fillers are generally considered safe and biocompatible, but they can cause local irritation, inflammation, or an allergic reaction in some individuals. In rare cases, the filler may also cause *_systemic reactions_*, such as anaphylaxis or cardiovascular problems.
Another potential complication of lip fillers is *_asymmetrical results_*, where one side of the face appears more swollen or uneven than the other. This can be caused by a variety of factors, including improper injection technique, varying levels of filler distribution, or underlying facial structure issues.
_*Lip filler migration*_ is another potential complication, where the fillers move away from their original placement and cause unevenness or asymmetry in the lips. This can occur due to *_rebound*_, where the skin springs back into its natural shape after the filler injection, or *_diffusion_*, where the filler spreads beyond its original area.
The use of lip fillers can also lead to *_scarring_*, particularly if the practitioner uses a needle that is too thick or causes excessive trauma to the surrounding tissue. In some cases, *_keloid formation_* may occur, which can be more noticeable in darker-skinned individuals.
Another consideration is the potential *_interference with future treatments_*. Using lip fillers that are not compatible with each other or with other cosmetic procedures can lead to unwanted results or complications.
The timing of lip filler dissolution can also vary depending on the type and concentration of the filler used. *_Reticulated hyaluronic acid_* (e.g., Restylane, Belotero) is more stable than *_non-reticulated HA_* (e.g., Juvederm), and *_calcium hydroxylapatite_* fillers (e.g., Radiesse) can take longer to break down.
Finally, it’s essential to consider the individual’s *_medication use_*, as certain medications can interact with lip fillers or increase the risk of complications. For example, *_platelet aggregation inhibitors_* (e.g., aspirin, clopidogrel) may increase the risk of bleeding or bruising during and after treatment.
In conclusion, evaluating the effectiveness of lip fillers requires a thorough understanding of the potential benefits and complications associated with their use. It’s essential to work with a qualified practitioner who has extensive experience with lip fillers and can provide personalized guidance on choosing the right filler for individual needs.
Side effects from using hyaluronidase for lip filler dissolution can include redness, swelling, and bruising. According to Dr. Jean Carruthers, “it is crucial that patients are aware of the potential risks and follow posttreatment instructions carefully to minimize complications.”
Hyaluronidase is an enzyme used to dissolve lip fillers, such as those made from hyaluronic acid, collagen, or calcium hydroxylapatite. The process of dissolving the filler involves injecting a small amount of hyaluronidase into the lip area, where it breaks down the filler molecules into smaller fragments that can be absorbed by the body.
When used for lip filler dissolution, hyaluronidase is typically administered in a series of injections, and the entire process can take anywhere from 15 minutes to several hours, depending on the size and location of the fillers. It’s essential to follow posttreatment instructions carefully, as recommended by your healthcare provider or dermatologist.
It’s crucial that patients are aware of the potential risks associated with hyaluronidase injection, including redness, swelling, and bruising. These side effects can range from mild to severe and may vary in duration, depending on individual factors such as skin type, age, and overall health.
According to Dr. Jean Carruthers, a renowned dermatologist and expert in cosmetic procedures, “it is crucial that patients are aware of the potential risks and follow posttreatment instructions carefully to minimize complications.” This emphasizes the importance of choosing a qualified healthcare provider who has experience with hyaluronidase injection and can guide you through the process.
Redness and swelling typically resolve on their own within a few days, but may be more noticeable in the first 24-48 hours after treatment. Bruising can take longer to fade and may be more persistent. In some cases, patients may experience more severe reactions, such as infection or allergic responses, which require immediate medical attention.
It’s also worth noting that hyaluronidase injection may not always completely eliminate the lip filler, especially if the fillers have been in place for an extended period or are located in areas with significant fatty tissue. In some cases, residual filler material may remain at the treatment site, which can cause prolonged swelling and redness.
Overall, while hyaluronidase is a safe and effective enzyme for dissolving lip fillers, patients should be aware of the potential risks and take steps to minimize complications. By choosing a qualified healthcare provider, following posttreatment instructions carefully, and reporting any concerns or adverse reactions promptly, you can help ensure a successful and complication-free lip filler dissolution treatment.
Read more about Melissa Neufeld here. Read more about The First Come First Served here. Read more about Decléor Direct here. Read more about Canniant here.
- Xela Rederm Skin Booster Treatments Near Surbiton, Surrey - February 3, 2026
- Xela Rederm Skin Booster Treatments Near Epsom, Surrey - February 2, 2026
- Why Vista Edge Vape Stands Out Among Premium Vape Brands - January 31, 2026
